CHRONIC PAIN? YOU FOUND HOPE: THE ALTMAN METHOD




"The Altman Method is not an abstract philosophy but a practical, reproducible framework that integrates structural integrity, biochemistry, neurology, and energy. It gives patients answers where they have only been dismissed, and it gives providers tools where they have only had protocols."
- Dr. Steven Murphy
Heal Injuries--Not Just What Shows up on Scans
Chronic pain isn’t a life sentence.
It’s a signal your body hasn’t been decoded yet.
The Altman Method is a systems-based approach that activates your body’s own repair mechanisms — even when imaging is “normal” and other treatments have failed.
This isn’t pain management.
This is precision medicine for repair.
End Chronic Pain • Avoid Unnecessary Surgery • Restore Confidence in Your Body
“I was told my scans were normal.
My pain wasn’t.
Dr. Altman found what everyone else missed — and fixed it.”
-70 Year Old Fibromyalgia Patient and Vietnam War Veteran
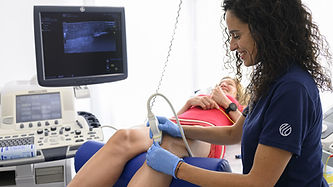
What is AltPoint Percutaneous Needle Electrolysis (PNE) or Ultrasound-Guided Galvanic Electrolysis Technique (USGET)
AltPoint delivers a low-intensity galvanic electrical current directly to dysfunctional tissue using ultrasound guidance, triggering controlled inflammation, clearing degeneration, and stimulating true cellular repair.
AltPoint™ PNE / USGET
A Precision-Based, Regenerative Approach to Healing Pain at Its Source
Chronic pain doesn’t happen “for no reason.”
In most cases, it stems from damaged, degenerated, or poorly healed connective tissue—ligaments, tendons, fascia, or joint capsules that never fully recovered after injury, stress, or trauma.
AltPoint™ Percutaneous Needle Electrolysis (PNE)—also known as Ultrasound-Guided Galvanic Electrolysis Therapy (USGET)—is a breakthrough treatment developed by Dr. Sean Altman to help the body restart the healing process where it stalled.
Rather than masking symptoms, AltPoint is designed to repair the underlying tissue, restore stability, and help patients return to active, confident living.
What Is the AltPoint™ Device?
AltPoint™ is a clinician-designed, ultra-precise regenerative needling device that delivers a gentle electrical current through a fine needle directly into injured tissue—guided by real-time ultrasound for accuracy and safety.
Unlike injections or surgery, AltPoint:
-
Does not inject medications, steroids, PRP, or cells
-
Uses the body’s own biology to stimulate repair
-
Is minimally invasive with very little downtime
-
Can be used for both acute and long-standing injuries
How AltPoint™ Works?
When tissue has been injured for weeks, months, years, healing can become “stuck.”
AltPoint helps unstick the process through several powerful mechanisms:
🔹 1. Precision Targeting
Using ultrasound, Dr. Altman places the needle exactly into the damaged ligament, tendon, or scar tissue—not just the painful area.
🔹 2. Restarting Healing
The gentle electrical current resets chronic inflammation, signaling the
body that repair is needed again.
🔹 3. Stronger Tissue Formation
AltPoint stimulates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen,
helping rebuild tissue that is stronger, more organized, and more resilient.
🔹 4. Improved Blood Flow & Cellular Energy
The treatment improves micro-circulation and local cellular activity,
supplying oxygen and nutrients where healing is needed most.
🔹 5. Neurological “Reset”
AltPoint helps calm irritated nerves and restores proper communication
between muscles, joints, and the brain—improving control, stability,
and confidence in movement.
Conditions Treated with AltPoint™
AltPoint has been successfully used to treat a wide range of musculoskeletal and ligament-based conditions, including:
-
Chronic tendon injuries (Achilles, rotator cuff, elbow, knee)
-
Ligament laxity and instability
-
Labral tears (hip and shoulder)
-
Meniscus tears
-
Plantar fasciitis
-
SI joint dysfunction
-
Post-surgical scar tissue and adhesions
-
Craniocervical Instability (CCI)
Healing timelines typically range from 4–8 weeks, often with only two treatments, depending on the condition.
Real-World Results: AltPoint Case Outcomes
Across 50 documented patient cases, AltPoint has demonstrated:
-
Pain reduction from 8–10/10 → 0–1/10
-
Strength improvements of 40–65%
-
Healing confirmed by musculoskeletal ultrasound
-
Return to sport, work, and daily activities
-
Resolution of injuries previously told they “would not heal”
Selected Examples:
-
Achilles tear: Fully healed by 8 weeks; returned to running
-
Hip labral tear: Pain resolved in 6 weeks
-
Shoulder labrum: Avoided surgery and returned to swimming
-
Meniscus tear: Full knee function restored
-
Chronic elbow tendinopathy: Grip strength fully restored
Craniocervical Instability (CCI)
Craniocervical Instability (CCI) occurs when the ligaments that stabilize the skull on the upper cervical spine become lax or damaged—most commonly the alar and transverse ligaments.
This instability can lead to:
-
Headaches and neck pain
-
Dizziness or imbalance
-
Brain fog and fatigue
-
Visual disturbances
-
Neurological symptoms
-
Difficulty holding alignment after chiropractic care
CCI may develop after:
-
Whiplash or concussions
-
Auto accidents or sports injuries
-
Connective tissue disorders
-
Repetitive postural stress
AltPoint™ for CCI: A New Option for Healing
Dr. Altman has now used AltPoint™ to help more than 50 patients with CCI, many of whom were previously told that surgery—or extremely expensive regenerative injections—were their only options.
AltPoint for CCI:
-
Uses ultrasound guidance to precisely target the alar and transverse ligaments
-
Typically requires two treatments
-
Supports ligament strengthening and stability
-
Has a healing timeline of 6–8 weeks
-
Is far less invasive and more affordable than alternative procedures
Patients often report:
-
Improved neck stability
-
Reduced neurological symptoms
-
Better ability to hold alignment
-
Improved confidence and function
Why Dr. Altman’s Approach Is Different
AltPoint is not a standalone treatment—it is part of The Altman Method, a systems-based approach that integrates:
-
Precision diagnostics
-
Ultrasound-guided interventions
-
Neuromuscular re-education
-
Proprioceptive retraining
-
Long-term tissue resilience strategies
This is why outcomes are not just fast—but durable.
A Final Word
AltPoint™ exists because too many people were told:
-
“You’ll have to live with it.”
-
“It won’t heal.”
-
“Surgery is your only option.”
-
For many patients, that simply isn’t true.
-
If you are dealing with chronic pain, instability, or an injury that never fully healed, AltPoint may offer a safe, effective, and regenerative path forward.







PNE/USGET Key Studies
-
Abat F, Diesel WJ, Gelber PE, Polidori F, Monllau JC, Sanchez-Ibanez JM. Effectiveness of the intratissue percutaneous electrolysis (EPI) technique and iso-inertial eccentric exercise in patellar tendinopathy at two years follow-up. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(2):188-193.
-
Abat F, Gelber PE, Polidori F, Monllau JC, Sanchez-Ibanez JM. Clinical results after ultrasound-guided intratissue percutaneous electrolysis (EPI) and eccentric exercise in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(4):1046-1052.
-
Arias-Buría JL, Truyols-Domínguez S, Valero-Alcaide R, Salom-Moreno J, Atín-Arratibel MA, Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis and eccentric exercises for subacromial pain syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:315219.
-
Arias-Buría JL, Truyols-Domínguez S, Valero-Alcaide R, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis as an adjunct to exercise and manual therapy for subacromial pain syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. J Pain. 2018;19(10):1107-1116.
-
Asensio-Olea L, Leirós-Rodríguez R, Marqués-Sánchez MP, Oliveira de Carvalho F, Maciel LYS. Efficacy of percutaneous electrolysis for the treatment of tendinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2023;37(6):747-759.
-
Augustyn D, Paez A. The effectiveness of intratissue percutaneous electrolysis (EPI) for the treatment of tendinopathy: a systematic review. S Afr J Sports Med. 2022;34(1):1-5.
-
Borrella-Andrés S, Malo-Urriés M, Pérez-Bellmunt A, et al. Application of percutaneous needle electrolysis does not elicit temperature changes: an in vitro cadaveric study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(23):15738.
-
Calderón-Díez L, Diesel WJ, Gelber PE, Polidori F, Monllau JC, Sánchez-Ibáñez JM. Prospective analysis of EPI plus eccentric exercise in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2021;4(2):188-193.
-
Calderón-Díez L, Sánchez-Sánchez JL, Robles-García M, et al. Cadaveric and ultrasound validation of a percutaneous electrolysis approach at the Achilles tendon: a pilot study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(19):11906.
-
Doménech-García V, Pecos-Martín D, Blasco-Abadía J, Bellosta-López P, López-Royo MP. Placebo and nocebo effects of percutaneous needle electrolysis and dry needling: a three-arm randomized double-blinded trial in patellar tendinopathy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1381515.
-
Fakontis C, Iakovidis P, Lytras D, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous needle electrolysis versus dry needling in musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(4):715-726.
-
Fernández-Rodríguez T, Fernández-Rolle A, Truyols-Domínguez S, et al. Prospective randomized trial of electrolysis for chronic plantar heel pain. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(9):1039-1046.
-
García-Vidal JA, Salinas J, Escolar-Reina P, et al. Galvanic current dosage and bacterial concentration are determinants of the bactericidal effect of percutaneous electrolysis: an in vitro study. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18977.
-
García-Vidal JA, Salinas J, Ortega N, et al. In vitro bacteriological effect of tri-beveled needle electrolysis against Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep. 2022;12:11468.
-
Gómez-Chiguano GF, Navarro-Santana MJ, Cleland JA, et al. Effectiveness of ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Med. 2021;22(5):1055-1071.
-
Gonzalez-Perez LM, Vera-Martin R, Montes-Latorre E, et al. Botulinum toxin and percutaneous electrolysis for chronic masticatory myalgia. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(4):278.
-
Góngora-Rodríguez J, Rosety-Rodríguez MA, Rodríguez-Almagro D, et al. Structural and functional changes in supraspinatus tendinopathy through percutaneous electrolysis, nerve stimulation, and eccentric exercise: a randomized clinical trial. Biomedicines. 2024;12(4):771.
-
Hissa ML, Araújo GA, De-La-Cruz-Torres B. Effectiveness of percutaneous needle electrolysis to reduce pain in tendinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Rehabil. 2024;33(5):307-316.
-
Iborra-Marcos Á, Ramos-Álvarez JJ, Rodríguez-Fabián G, et al. Intratissue percutaneous electrolysis versus corticosteroid infiltration for plantar fasciosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(6):704-711.
-
Jiménez-Rubio S, Oliva-Pascual-Vaca J, Rodríguez-Blanco C, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis and rehabilitation following hamstring injury reduces return-to-play time in professional soccer: a case series. J Invasive Tech Phys Ther. 2020;3(1):38-45.
-
López-Martos R, González-Perez LM, Ruiz-Canela-Méndez P, et al. Percutaneous electrolysis versus dry needling in temporomandibular myofascial pain: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018;23(4):e454-e462.
-
López-Royo MP, Ríos-Díaz J, Galán-Díaz RM, et al. Comparative study of interventions for patellar tendinopathy: a randomized trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(5):967-975.
-
Ramos-Barbero M, Pérez-Jiménez A, Serrano-Carmona S, et al. Percutaneous electrolysis and nutritional factors in induced tendinopathy: an animal study. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(13):7315.
-
Rodríguez-Huguet M, Góngora-Rodríguez J, Rodríguez-Huguet P, et al. Effectiveness of percutaneous needle electrolysis in supraspinatus tendinopathy: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1837.
-
Rodríguez-Huguet M, Góngora-Rodríguez J, Lomas-Vega R, et al. Percutaneous needle electrolysis in chronic lateral epicondylalgia: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2068.
-
Rodríguez-Sanz J, Rodríguez-Rodríguez S, López-de-Celis C, et al. Biological and cellular effects of percutaneous electrolysis: a systematic review. Biomedicines. 2024;12(12):2818.
-
Sánchez-González JL, Navarro-López V, Cañada-Sánchez P, et al. Efficacy of different intensities of percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1178466.
-
Sánchez-González JL, Navarro-López V, Calderón-Díez L, et al. Effectiveness of different percutaneous electrolysis protocols in endogenous pain modulation: a randomized controlled trial. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2023;68:102872.
-
Tavares-da-Silva AC, Barroso-Barrosen F, Moreira-Marcos A, Silva-Lima A. Effect of percutaneous electrolysis on pain and disability in tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2024;40:134-144.
-
Valera-Garrido F, Minaya-Muñoz F, Medina-Mirapeix F. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis in chronic lateral epicondylitis: short-term and long-term results. Acupunct Med. 2014;32(6):446-454.
-
García Naranjo J, Barroso Rosa S, Loro Ferrer J, et al. A novel approach in the treatment of acute whiplash syndrome: ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(8):1229-1234.
-
De-la-Cruz-Torres B, Barrera-García-Martín I, Valera-Garrido F, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis in dancers with chronic soleus injury: a randomized clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:4156258.
-
Martínez-Silván D, Santomé-Martínez F, Champón-Chekroun A, et al. Clinical use of percutaneous needle electrolysis in musculoskeletal injuries: a systematic review. Apunts Sports Med. 2022;57:100396.
-
Varela-Rodríguez S, Sánchez-Sánchez JL, Velasco E, et al. Endogenous pain modulation in response to a single session of percutaneous electrolysis in healthy individuals: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Med. 2022;11(10):2889.
-
Valera-Garrido F, Margalef R, Bosque M, et al. Percutaneous needle electrolysis accelerates functional muscle regeneration in mice. Appl Sci. 2022;12(19):10014.
-
Gómez-Chiguano GF, Navarro-Santana MJ, Cleland JA, et al. Effectiveness of ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Med. 2021;22(5):1055-1071.
-
Rodríguez-Sanz J, Rodríguez-Rodríguez S, López-de-Celis C, et al. Biological and cellular effects of percutaneous electrolysis: a systematic review. Biomedicines. 2024;12(12):2818.
-
Sánchez-González JL, Navarro-López V, Cañada-Sánchez P, et al. Efficacy of different intensities of percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1178466.
-
Doménech-García V, Pecos-Martín D, Blasco-Abadía J, et al. Placebo and nocebo effects of percutaneous electrolysis and dry needling in patellar tendinopathy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1381515.
-
Calderón-Díez L, Diesel WJ, Gelber PE, et al. Prospective analysis of intratissue percutaneous electrolysis plus eccentric exercise in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2021;4(2):188-193.
-
Asensio-Olea L, Leirós-Rodríguez R, Marqués-Sánchez M, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous electrolysis for the treatment of tendinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2022;36(12):1528-1540.
-
Gómez-Chiguano GF, Navarro-Santana MJ, Cleland JA, et al. Effectiveness of ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain. Pain Med. 2021;22(5):1055-1071.
-
Iborra-Marcos Á, Ramos-Álvarez JJ, Rodríguez-Fabián G, et al. Intratissue percutaneous electrolysis versus corticosteroid infiltration for plantar fasciosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(6):704-711.
-
López-Martos R, González-Perez LM, Ruiz-Canela-Méndez P, et al. Randomized double-blind comparison of percutaneous electrolysis and dry needling for temporomandibular myofascial pain. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018;23(4):e454-e462.
-
Valera-Calero J, Sánchez-Mayoral-Martín A, Varol U. Short-term effectiveness of high- and low-intensity percutaneous electrolysis in patellofemoral pain syndrome: a pilot study. World J Orthop. 2021;12(10):781-790.
-
Varela-Rodríguez S, Sánchez-González JL, Sánchez-Sánchez JL, et al. Effects of percutaneous electrolysis on endogenous pain modulation: study protocol. Brain Sci. 2021;11(6):801.
-
De-la-Cruz-Torres B, Barrera-García-Martín I, Valera-Garrido F, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis in dancers with chronic soleus injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:4156258.
-
Martínez-Silván D, Santomé-Martínez F, Champón-Chekroun A, et al. Clinical use of percutaneous needle electrolysis in musculoskeletal injuries. Apunts Sports Med. 2022;57:100396.
-
Rodríguez-Sanz J, Rodríguez-Rodríguez S, López-de-Celis C, et al. Biological and cellular effects of percutaneous electrolysis: a systematic review. Biomedicines. 2024;12(12):2818.
-
Sánchez-González JL, Navarro-López V, Cañada-Sánchez P, et al. Efficacy of different intensities of percutaneous electrolysis for musculoskeletal pain. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1178466.
-
Doménech-García V, Pecos-Martín D, Blasco-Abadía J, et al. Placebo and nocebo effects of percutaneous needle electrolysis and dry-needling in patellar tendinopathy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1381515.
-
Calderón-Díez L, Diesel WJ, Gelber PE, et al. Prospective analysis of EPI plus eccentric exercise in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2021;4(2):188-193.
-
Valera-Garrido F, Margalef R, Bosque M, et al. Percutaneous needle electrolysis accelerates functional muscle regeneration in mice. Appl Sci. 2022;12(19):10014.
-
García Naranjo J, Barroso Rosa S, Loro Ferrer J, et al. A novel approach in the treatment of acute whiplash syndrome: ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrolysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(8):1229-1234.
-
Varela-Rodríguez S, Sánchez-Sánchez JL, Velasco E, et al. Endogenous pain modulation in response to a single session of percutaneous electrolysis in healthy population: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Med. 2022;11(10):2889.
👉 Book Your Evaluation and discover how advanced, targeted therapies can unlock your body’s ability to heal—without unnecessary surgery or endless “management” plans.